Welcome to the second installment of our Beginner’s Guide to Planet Zoo series! In this guide, we will explore the fundamentals of constructing your very own zoo, including aspects such as terrain, habitats, and amenities.
If you’re just starting with this series, be sure to check out our introductory guide on the fundamentals of Planet Zoo.
To see the process of zoo construction in action, check out our video featuring Principal Pipeline Artist, Liesa, as she explores the building aspects of Planet Zoo: Console Edition.
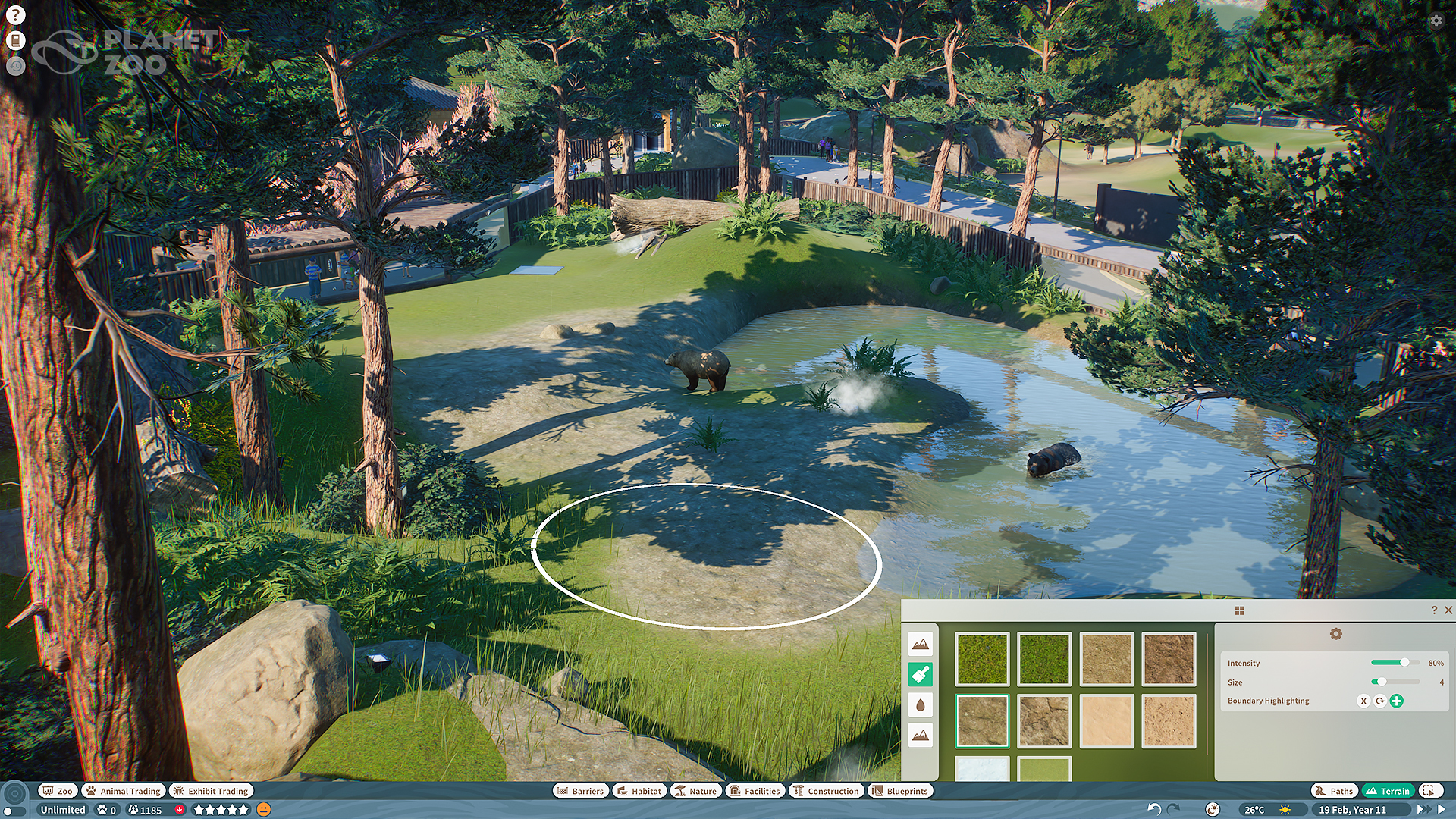
The environment of your zoo is entirely adjustable, featuring tools for shaping and painting the terrain, enabling you to tailor the zoo to your preferences.
Landscape Shaping
Contents
- 1 Environments and Displays
- 2 Paths
- 3 Power
- 4 Water Purification
- 5 Employee Amenities
- 6 Amenities for Guests
Terrain sculpting enables you to alter the height and contours of the landscape in your zoo, allowing you to create hills, level out spaces, and design picturesque views for your exhibits and attractions. Certain modes provide the option to begin with a flat landscape for construction or to modify an existing sculpted area.
All sculpting instruments can be adjusted by changing the intensity and size settings of the terrain brush, which will impact the speed and extent of the modifications applied to the landscape.
Tools for shaping terrain consist of:
- Push and Pull techniques can be utilized to elevate or depress the landscape.
- Flatten to Foundation – This tool levels all terrain within the selected circle to the height of the foundation. It is ideal for swiftly preparing ground areas to match an existing height.
- Flatten to Surface – Similar to Flatten to Foundation, this method utilizes a specific location as a foundation while also considering the orientation, enabling the effortless creation of slopes or steep cliffs.
- Chisel – Utilizes the position and angle of a point to eliminate terrain within that plane. This tool is beneficial for establishing uniform slopes.
- The smooth feature is beneficial for refining landscapes, as it aids in eliminating jagged edges and creates more gentle contours.
- Roughen – This term refers to the contrast of Smooth; apply it to enhance the unevenness and diversity of the landscape, resulting in a textured appearance.
- Flatten to Terrace – This technique levels elevated ground in specified increments to create flat surfaces while maintaining some degree of height variation. It is beneficial for preparing areas for construction on slopes or for designing expansive water features of varying depths for wildlife.
- The Terrain Stamp Tool offers a different method for modifying terrain, featuring five distinct shapes. By enabling the ‘Subtract terrain’ option in the Stamp Mode settings, users can utilize the shape to eliminate terrain rather than to create it.
Landscape Artistry
The landscape of your zoo significantly influences its appropriateness for various animal species and their overall well-being in their environments. You can discover the unique terrain needs and preferences for each species in the Zoopedia.
There are six fundamental types of terrain:
- Grass
- Tall grass
- Soil types (light and heavy)
- Stone (polished/rough)
- Gravel (fine/coarse)
- Snow will only accumulate on the ground when the temperature is sufficiently low.
Animals do not differentiate between various kinds of rock, soil, or sand. If they have a preference for sand, they will accept both fine and coarse varieties. However, they do have preferences when it comes to grasses and may favor certain types in varying amounts. Therefore, it’s important to consult the Zoopedia and keep an eye on their happiness within their environment.
Incorporating Water
Water plays a crucial role in the lives of numerous animals and is a vital consideration in zoo design. A variety of species require access to water for swimming, cooling off, and hydration. When water is a critical component of an animal’s habitat, it will be indicated, along with any spatial needs, in the Terrain section of the animal’s information panel.
Incorporating water is an easy task:
- Establish an area to hold the water, such as by forming a depression or lakebed using the Terrain Tools.
- Mark the spot on the wall indicating the level to which the water should be filled.
- Choose to complete.
- When water can be added, the height indicator will turn blue. If it shows red, it means that water placement is not allowed.
After adding water, you can choose it in two distinct ways for customization: either approach the water body directly to select it, or activate the ‘water selection’ mode through the terrain browser.
The hue of specific bodies of water can be modified using the flexicolour system. Additionally, the clarity of the water can be altered, allowing for options ranging from very murky to perfectly clear. Any personalized water color configuration is stored, but it can be reset to the original color by using the ‘Use natural color’ switch.
Over time, water in an environment inhabited by animals will become contaminated. However, you have the option to intentionally pollute the water if you choose to do so. Keep in mind, though, that unfiltered water can heighten the risk of infection in animals, so it’s advisable to maintain cleanliness by utilizing a water treatment system whenever feasible.
Environments and Displays

In Planet Zoo, you can find two types of habitats for animals:
- Habitats serve as living spaces for larger creatures such as aardvarks and West African lions. They consist of a habitat barrier and a habitat gate.
- Exhibits are specialized enclosures designed for small creatures such as the goliath beetle or the green iguana. Unlike habitats, which can accommodate multiple species, an exhibit functions as an independent vivarium, allowing for the housing of only a single species at a time.
Creating a Simple Habitat
A fundamental habitat is made up of a habitat barrier and a habitat entrance. To establish a habitat:
- Access the barrier modification tool.
- Choose an appropriate type of wall to accommodate your pet.
- Construct a wall loop to form an enclosed area.
- Once you have formed a full loop, choose the ‘Habitat Gate’ from the object list.
- Ultimately, position the habitat gate in a way that the pathway extends outward from the habitat.
You can initiate the construction of your habitat by positioning the gate and expanding from there. If the gate’s location doesn’t meet your satisfaction, you have the option to relocate it along the wall.
An animal must fulfill all of its needs in order to be situated in its environment.
Factors that could render a habitat unsuitable include:
- The barrier loop is discontinuous.
- The barrier lacks a gate for keeping it secure.
- The barrier loop contains multiple keeper gates.
- The environment is situated within a different environment.
Once a fundamental habitat has been established, the subsequent actions involve obtaining the following items:
- Commerce Hub
- Keeper
- Guardian’s shelter
- Energy supply
After establishing these elements, make sure that all facilities, including the habitat entrance, are linked by pathways and are supplied with power as needed.
There you go, you now possess a fundamental environment suitable for an animal!
Barriers

Numerous types of barriers can be utilized to create an ideal habitat, with each offering its own advantages and disadvantages.
Suitability of Barriers
When evaluating a barrier type for a specific animal, the two key factors to consider are the level of resistance and the animal’s climbing ability.
- The resistance rating reflects the strength of a wall and the types of animals it can effectively contain. While it might be feasible to use a barrier with a lower rating to contain an animal, there is a significant risk of it failing, potentially allowing the animal to escape.
- Climbing status – denotes if the wall is accessible for animals to climb prior to the implementation of further climbing deterrents.
The transparency of the barrier determines if visitors can observe the animals in their environment. It also reveals if the animals can see the visitors, which may lead to stress for the animals if they are being watched.
Barriers designated as watertight are effective for containing large amounts of water.
Degradation of Barriers
Aside from hedges, electric fences, and null barriers, all other types of barriers utilized as habitat perimeters will experience degradation over time, and the speed of this deterioration will vary based on the materials used in the construction of the wall.
As a barrier deteriorates, its effectiveness diminishes, and eventually, it may weaken to the point where an animal can break free. If the barrier deteriorates entirely, it will fall apart, allowing any animal that approaches it to escape.
Barriers visibly indicate their wear and tear, but the precise condition of these barriers within a habitat can also be monitored through the Habitat Info panel. Mechanics can fix barriers during their regular inspections or when they are specifically summoned to the habitat.
Types of Gates
Three varieties of gates can be incorporated into a habitat wall:
- Habitat Gate – Utilized by zookeepers, veterinarians, technicians, and maintenance staff.
- Guest Gate – Utilized by visitors and personnel moving throughout the habitat.
- Airlock Track – Utilized by transportation rides. An internal track is necessary within the habitat.
Incorporating Windows
Windows provide a way for visitors to observe the animals, and numerous walls are designed to accommodate them. Check the window settings and choose between windowed or one-way glass options. If the one-way glass is oriented incorrectly, you can adjust its direction. This type of window enables guests to see the animals while minimizing stress for the animals themselves.
Incorporating Climbproof Defense
To enhance escape prevention, climbproofing features can be incorporated into certain walls. After choosing the wall, locate the climbproof option and adjust it to the left, right, or both sides. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where two enclosures are separated by a common barrier.
Height of the Barrier
In addition to the typical feature of modifying barrier heights, there are several other options to explore, as outlined below:
- Height Snap enables you to modify wall height with exact precision.
- Snap to Adjacent Height is enabled by default, aligning a barrier’s height with that of its neighboring structures. This feature can be turned off for greater precision in height adjustments.
As obstacles are established, the conduct of the new segments can be modified through the following actions:
- The wall’s upper edge follows the natural contours of the landscape, maintaining a uniform height throughout.
- Flat Top – The wall’s height is adjusted to ensure a uniform top surface, irrespective of the variations in the ground’s elevation.
- Flat Top and Adjustable Bottom – Similar to the previous option, but with the added feature of being able to pull the barrier downwards, possibly beneath the ground, to facilitate the construction of barriers on irregular terrains.
Zero Barriers
Null barriers serve to establish a habitat boundary without the need for a tangible fence. Animals can easily traverse a null barrier and may escape if the opportunity arises. Therefore, it is essential to implement them alongside additional features like cliffs, water bodies, or ha-ha ditches.
Null barriers offer an unobstructed perspective for visitors and enable habitat development in spaces where walls may be undesirable or impractical, eliminating the need for wall installation.
Heating and Cooling Devices
Heaters and coolers both need energy to modify the surrounding temperature. When the device is positioned, it activates the Temperature view mode, demonstrating its impact on the environment. When adjusting the temperature on the heater or cooler, consider the workload you’re imposing on it; the more you deviate from the ambient temperature, the higher the continuous operating expenses will be.
Water Temperature Controller
Water Temperature Regulators are designed to gradually adjust the temperature of the connected water bodies to a specified target temperature. The process will take more time for larger bodies of water. The temperature will not drop below the freezing point. When the device is positioned, it will activate a view mode that demonstrates its impact on the nearby water.
Wildlife Escapes

Animals flee when they successfully exit their natural environment. The primary factors contributing to their escape include:
- The creature has either ascended or leaped out.
- The creature has traversed an empty boundary.
- The creature has navigated past a shallow obstruction in the water.
- A gap has formed in their protective wall, possibly due to wear and tear or as a result of the animal breaking through.
An animal will try to flee if it has the opportunity to do so.
What is Considered an Escape?
A boundary can take the form of a wall or a simple line in the ground, but every ecosystem has its limits. When an animal goes beyond these limits, it is deemed to have escaped. This holds true even if the animal moves from one ecosystem to another; as long as it is outside its designated habitat, it is regarded as having escaped.
Consequences of Fleeing
When an animal manages to break free, it experiences stress, which negatively impacts its well-being. Visitors are not interested in witnessing an animal in a state of escape, and if the animal is perceived as a threat, guests are likely to leave the zoo in a hurry.
Bouncing Back After Escapes
Animals that have fled must be apprehended by a veterinarian. Such escapes are considered urgent matters, and the veterinarian will strive to catch the animal at the earliest opportunity. If the animal’s original environment is still intact, the veterinarian will return the escaped animal to that location.
Avoiding Breakouts
Review the Zoopedia to ensure you have adequate barriers in place.
- Ensure that the wall reaches a sufficient height.
- Ensure that the wall has sufficient strength.
- Ensure that the wall is well-maintained.
- If the animals are capable of climbing, ensure that you have barriers that are impossible to scale or utilize walls that cannot be climbed.
- Refrain from placing items that can be climbed close to the fence.
Visitors and Environments
Visitors can observe animals by standing on a pathway, resting on a bench, or enjoying a ride on a transport vehicle. To spot an animal, they need a clear line of sight. Various factors, such as barriers, vegetation, and other objects, can obstruct the view, as can the distance separating the visitor from the animal. Strategically positioning windows, feeders, toys, and other elements within the habitat can help attract animals to more visible areas.
A visitor who cannot spot any animals will move to a different location in hopes of improving their sighting experience. If their efforts do not yield results after several tries, they will eventually abandon their pursuit of that particular animal. As visitors observe animals, they experience a boost in happiness, which varies based on the clarity of the view, with the most favorable views providing the highest levels of joy. Conversely, the happiness of the visitors will diminish if the animals they are watching appear to be in poor health.
Creating an Ideal Environment
Creating a simple habitat is straightforward, but designing one that satisfies both your animals and visitors can be a bit more challenging.
Establishing an effective environment involves:
- Ample room for your pets.
- Suitable landscape, vegetation, and ornaments for your animals.
- Suitable and properly maintained barriers to stop animals from escaping.
- An area for your pets to relax and enjoy some solitude.
- Proximal and manned establishments such as a caretaker’s cabin, electrical supply, and more.
- Impressive scenery for your visitors.
What is effective for one species may not be suitable for another, so it’s important to refer to the Zoopedia and try different methods to determine the most suitable care for your animals.
Exhibits

Exhibits are designated enclosures with solid walls designed to accommodate smaller animals designated as ‘exhibits.’
There are two categories of exhibits:
- 4m x 4m Display – designed for small animals, allowing visitors to observe them from every angle.
- 12m x 20m Interactive Exhibit – designed for animals exhibiting more intricate behaviors, allowing visitors to observe from within.
Each enclosure is designed to accommodate a single species at a time. Similar to the animals in their natural habitats, the exhibits and their residents are cared for by the staff.
Arranging Displays
For an exhibit to operate effectively, the following elements must be included:
- Display linked to a route.
- Commerce Hub
- Keeper
- Guardian’s shelter
- Energy supply
After an exhibit is set up, animals can be obtained through the Exhibit Trading interface and immediately placed into the exhibit.
Visitors and Displays
Similar to habitats, visitors will come to the exhibit window to observe the animals within, always favoring those that appear healthy and well-cared-for. To access a viewing area, the exhibit window needs to be linked to a pathway for guests. If a window is not linked or is marked as ‘closed’ in the ‘Windows’ section, visitors will be unable to see the animal and will not attempt to do so. In the case of larger walkthrough exhibits, guests can observe the animals from the interior pathway or from paths adjacent to the windows that are not marked as ‘closed’.
Paths

Paths serve as the essential link that unites all the facilities within the zoo. Without these pathways, both employees and visitors would struggle to move throughout the zoo. You can create paths by using the ‘paths’ menu.
- Choose the type of path using the browser.
- Position the pathways on the surface. If the placement is close to an existing path, a link will be established.
- Change the course of the path by indicating the preferred direction.
Whenever you position a segment of the path, you will advance and begin to position the subsequent segment. You can adjust the dimensions of the path segments to meet your requirements. Broader paths require a higher investment to install, but they can accommodate a greater number of visitors before experiencing congestion and delays.
Employee Journeys
Employee pathways are off-limits to visitors. These routes are designed to facilitate the smooth movement of staff throughout the zoo while ensuring that guests are kept away from staff-only areas that could detract from their experience.
Power
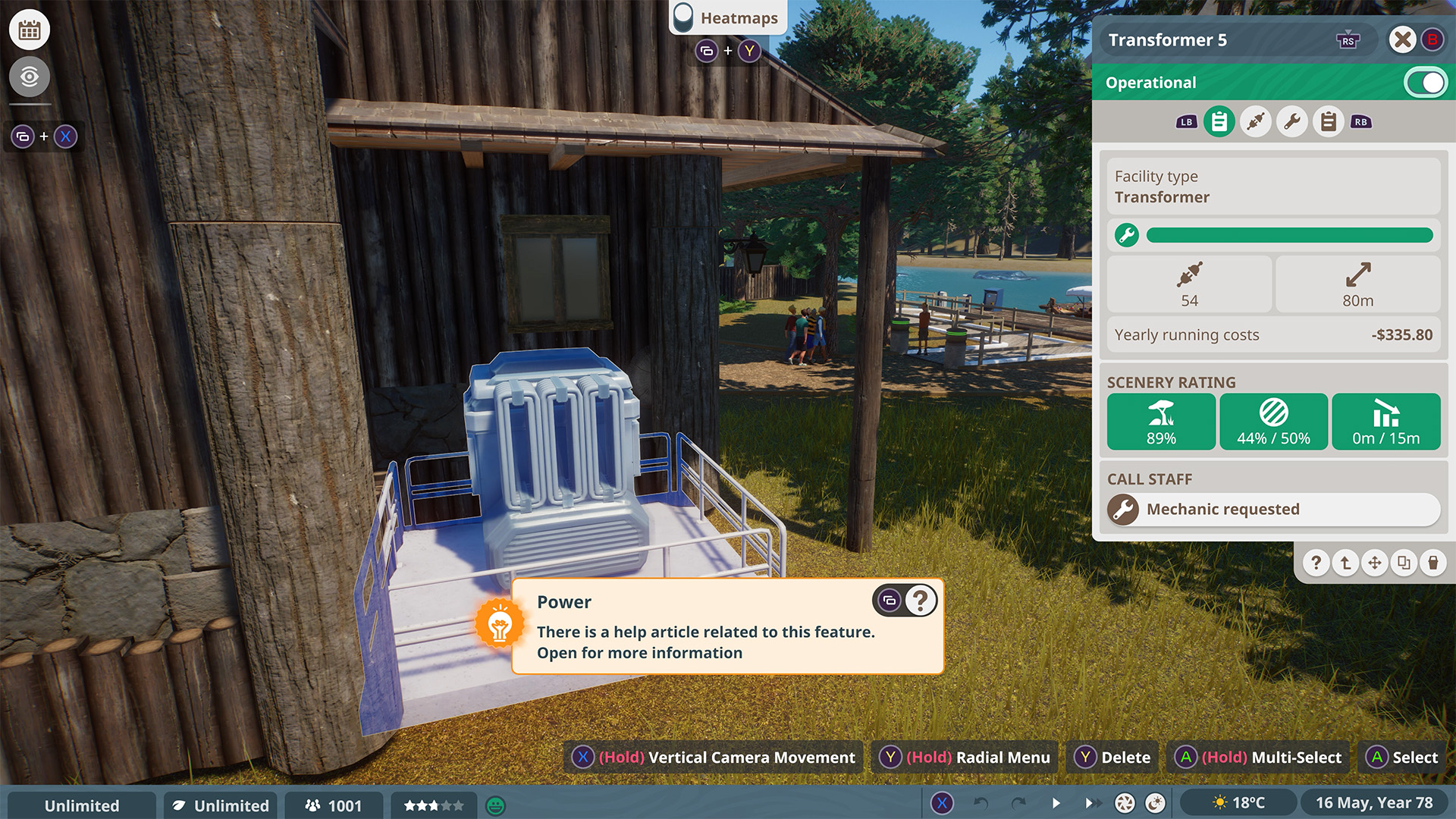
Numerous zoo operations rely on a consistent power source to function properly, making it crucial to ensure a reliable power supply for the zoo’s operations.
A power source can energize any object or environment that falls within its range, even if only a portion of it is included. Over time, power generation facilities will experience wear and a decline in efficiency. Among these, transformers exhibit greater durability compared to wind turbines, whereas solar panels tend to be the least robust.
When the efficiency of a power facility drops to 50%, its operational range begins to diminish. This decline could result in the facility ceasing to supply energy to essential operations, leading to their eventual breakdown. If the efficiency falls to 0%, the entire power system will cease to function.
There are several methods to supply energy to your facilities.
Transformers
They are relatively inexpensive to construct and offer an extensive operational range; however, they rely on non-renewable energy and incur operational expenses that depend on the quantity of devices they are energizing. Visitors are often unimpressed by the sight of transformers and may feel dissatisfied if they are visible; therefore, it’s advisable to position them out of sight to prevent this.
Wind Energy Generators
A renewable energy option that operates more effectively in windy and cooler environments. While their initial purchase price is higher than that of a transformer, they have no operational expenses. Visitors recognize the advantages of wind turbines, yet their noise levels result in a minor decrease in overall satisfaction.
Photovoltaic Modules
A renewable energy option that operates more effectively in hot, sunny environments. Similar to wind turbines, they require a higher initial investment compared to transformers, yet they incur no ongoing expenses. Visitors recognize the advantages of solar panels, making them generally indifferent to their installation.
The utilization of both types of renewable energy will enhance the zoo’s conservation status.
Water Purification

Water treatment plants are essential for maintaining the cleanliness of aquatic environments and rely on energy for their operations. Proper water treatment is crucial for the health of animals, ensuring they have access to safe drinking water and minimizing the risk of illness. Additionally, the clarity of the water enhances the experience for visitors, allowing for improved visibility of the animals.
Visitors are not thrilled by the sight of water treatment plants, and proximity to these facilities tends to dampen their spirits. A water treatment plant is capable of purifying any water source within its range, even if a portion of it lies beyond that range.
Water treatment plants experience a decline in performance as time passes. When a facility’s efficiency drops to 50%, its effective coverage area begins to diminish. This decline may result in a failure to purify water bodies. If efficiency falls to 0%, the water treatment system will cease to function entirely.
Employee Amenities

Staff facilities consist of the various structures utilized by employees to carry out their responsibilities. To operate effectively, all staff facilities need to be supplied with power and connected by pathways. Enhancing these facilities with surrounding scenery or additional structures can boost staff morale while they are present.
Guests prefer to avoid proximity to staff areas, so it’s advisable to locate these facilities at a distance from them. The intensity of this preference can differ depending on the specific facility.
Commerce Hub
The trade center serves as an entry point for animals entering the zoo. It plays a crucial role in the introduction of new animals. Those animals that arrive at the trade center will be temporarily housed, with their age and requirements paused, and can subsequently be either returned to their natural habitat or exchanged for money or Conservation Credits in Franchise Mode.
All adopted animals will be housed in the trading center, where a caretaker or veterinarian will gather them and deliver them to the specified location upon request. The trading center features distinct facilities for animals in their natural habitats, those for display, and animals that have been rewarded.
Once the capacity is reached, no additional animals can be adopted or offered for sale.
Guardian Cabin
Keeper huts serve as the sole area within a zoo designated for the preparation of animal food, making them essential for the well-being of the animals.
Keeper huts are available in two different sizes, influencing the number of keepers who can cook at the same time. This is based on the facility’s ‘capacity,’ which can be located on its information panel.
The placement of keeper huts is crucial, as the proximity of the hut to the habitat entrance or exhibit influences the amount of walking the keeper must undertake during the food preparation process.
Employee Lounge
Staff rooms are designated spaces where employees can relax and recharge before resuming their responsibilities.
Employees who do not take breaks will become less productive and may ultimately leave their positions. The staff room has a restricted capacity based on the building’s design, allowing only a specific number of staff members to utilize the space simultaneously.
If the staff room is either without power or at capacity, employees will line up outside until it is available for use.
Training facilities for employees are essential for their development and can also serve as a space for employee benefits.
They incur annual operating expenses and provide particular advantages to employees who take breaks in that location.
Quarantine
Quarantine serves as a secure method for separating ill animals prior to their treatment at a veterinary clinic. Additionally, it is utilized to evaluate new animals arriving at the zoo before they are placed in their designated habitats. There are two distinct sizes of quarantine facilities, each with varying capacities.
Veterinary Surgery
The veterinary clinic serves as the sole facility where veterinarians can address illnesses and injuries in animals. Operating without a veterinary clinic poses significant risks. At any moment, only a single animal can receive treatment in the clinic.
Research Facility
The veterinary research facility enhances the zoo’s understanding of animal species. It comes in two sizes: a smaller facility that can support a single staff member and a larger one that can accommodate up to six personnel.
Workshop
The workshop serves as a research space for mechanics. It is designed in a single size and can host only one mechanic at a time.
Safety Equipment
- Surveillance cameras help deter criminal activity in their monitored locations. However, visitors may express concerns about excessive monitoring, so it’s important to consider their potential adverse effects on overall satisfaction.
- Signs that say ‘Do Not Feed the Animals’ will decrease the chances of visitors giving animals food meant for humans.
- ‘Do Not Disturb’ signs can minimize the chances of guests creating noise near the animals, which may help alleviate stress for those that are especially timid.
Amenities for Guests

Guest facilities are structures created to meet the requirements of visitors. Often, these facilities require electricity to operate. When they are situated in scenic locations, the enjoyment of both guests and staff is likely to be enhanced.
Zoo Entry Point
Zoo entrances mark the points where visitors enter and exit the zoo. They serve as a convenient initial power source that guests find acceptable to be close to. By choosing a zoo entrance, the information panel for that entrance is shown, allowing for the adjustment of ticket prices for both adults and children.
Extra entrances to the zoo can be constructed to help evenly distribute visitors in larger facilities. Visitors are required to go through a Zoo Entrance gate to buy a ticket and to move around, enter, or exit the zoo freely.
Grocery Stores
Every food establishment offers a distinct variety of cuisine, with some options potentially better suited to the zoo’s climate. For instance, visitors are likely to feel more satisfied after consuming hot meals in a chilly environment. To operate effectively, food shops require both energy and a vendor.<